
Biogas has been defined in various different ways;
All the definitions are in agreement that biogas is derived, produced or generated from decomposed waste materials, organic matter, waste water, and solid waste or plant crops. In absence of oxygen. Biogas is produced through the processing of various types of organic waste such as food waste, human waste, sewage, paper waste, manure, green waste, biodegradable plastic, and slaughterhouse.
Biogas production also helps in the easy disposal of organic wastes and is eco-friendly because combustion of biogas does not cause much pollution. It has high calorific value and is a non-polluting renewable source of energy Biogas production starts from the arrival of feed-stocks at the biogas plant.
ALL BIOGAS MODELS
BIOGAS AS AN ENERGY SOURCE
Biogas is a fuel gas produced by anaerobic fermentation of organic material by methane producing bacteria. Methane is produced in strictly anaerobic (oxygen-free) sealed conditions by particular bacteria consortium.
Biogas has the following characteristics.
- Generally, it contains 50-70% methane,
- Major gas component is methane (CH4), CO2 and H2O,
- Minor gas component is H2, N2 and H2S,
- It is carbon neutral
Biogas has calorific value similar to LPG and natural gas, although the value is only about half of that of fossil fuels. Biogas can be utilized in the same way as LPG or natural gas when modified cooking stoves or modified engine-generators are applied.
SERVICING YOUR BIOGAS

HOW TO EFFICIENTLY SERVICE AND MAINTAIN BIOGAS DIGESTER
Maintaining a biogas plant involves;
- Doing minor repairs to the equipment,
- Changing its oil as needed,
- Removing debris from organic matter that falls to the bottom of the tank,
- Solving problems in the process
- Removing debris from organic matter that falls to the bottom of the tank
- Breaking and removal of any scum formed at the top of the slurry.
- Leakage test trouble shooting along the gas line.
- Inspection of any elogged/blocked joints at the utilization point
- Check the air blower on monthly basis.
COMPARING BIOGAS FUELS
| FUEL TYPE | VALUE | UNIT | FORM |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPG | 92-94 | MJ/m3 | Gas |
| Methane | 35.9 | MJ/m3 | Gas |
| Natural Gas | 37-39 | MJ/m3 | Gas |
| Kerosene | 36.7 | MJ/L | Liquid |
| Diesel Oil | 37.7 | MJ/L | Liquid |
| Coal | 22-26 | MJ/Kg | Solid |
| Biogas | 20-30 | MJ/m3 | Gas |
| Firewood* | 10-20 | MJ/Kg | Solid |
There are two types of biogas systems depending on the moisture content of the feed-stocks;
- Wet biogas system– it’s the most common biodigester style. A wet biodigester or low solids AD system generally processes feedstock with less than 15 percent solids content
- Dry biogas system – Dry biodigesters keep the substrates in a stackable form and remain in a pile during the digestion process. Food waste is mixed with green wastes such as yard debris for structure and porosity and is put into a long, rectangular vessel in a stack. The vessel is then sealed tight and warmed.
BIOGAS PRODUCTION BOOSTER

Anaerobic digestion is a biological process during which complex organic matter is decomposed in the absence of oxygen, by various types of anaerobic microorganisms. (BUY Biogas Production Booster) Biogas booster can be used in houshehold biogas or industrial biogas production, just add the enzyme to get your biogas plant boosted over 50% more biogas produced!
BIOGAS ACCESSORIES
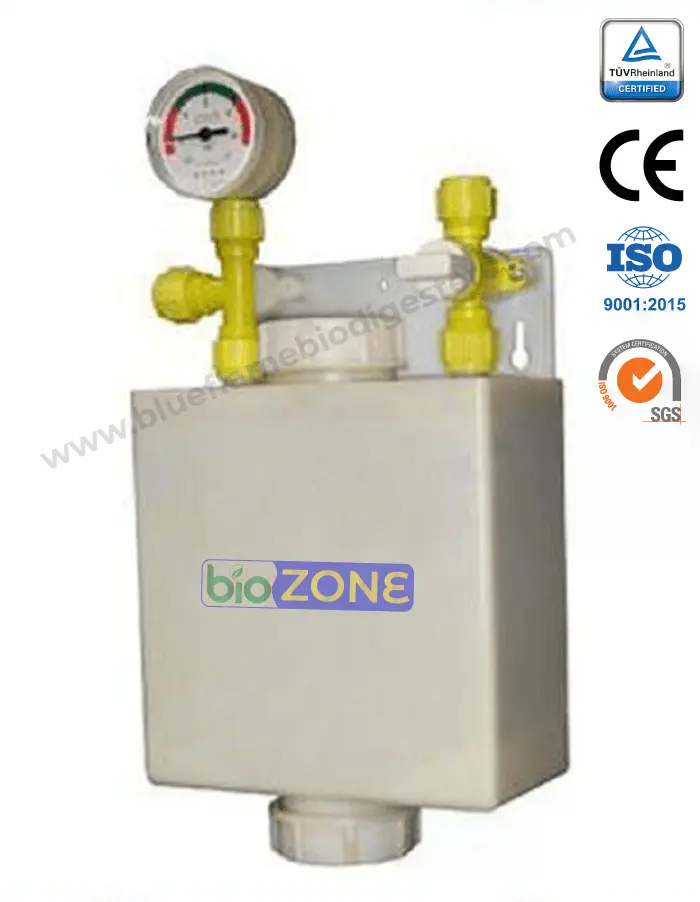

These conditions significantly affect bacterial activity
The rates of methane production are highly sensitive to temperature changes.
Generally, sulfate reduction also occurs in the biogas digester, producing hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide needs to be removed since it is corrosive and damages pipes, valves, meters, and engines and generators. (Buy Desulphiriser)
BIOGAS PRODUCTION BOOSTER

The raw materials used for the generation of biogas in our biodigesters include;
- Vegetable waste & Solid leftover food
- Milk products
- Roots, tubers, peels
- Livestock waste such as cow dung, poultry droppings, etc
OUR BIOGAS ACCESSORIES
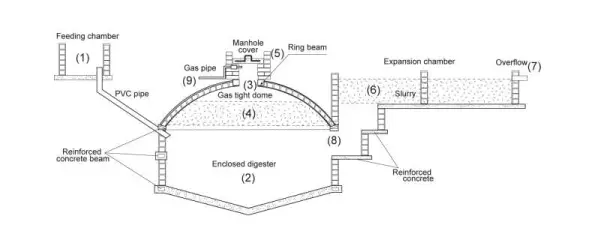
DIFFERENT TYPES OF BIOGAS
The table below gives a first comparison of the different types of biogas
| FACTORS | FIXED DOME | FLOATING DRUM | TABULAR DESIGN | PLASTIC CONTAINER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas storage | Internal Gas storage up to 20 m³ (large) | Internal Gas storage drum size (small) | Internal eventually external plastic bags | Internal Gas storage drum sizes (small) |
| Gas pressure | Between 60 and 120 mbar | Upto 20 mbar | Low, around 2 mbar | Low around 2mbar |
| Skills of contractor | High; masonry, plumbing | High; masonry, plumbing, welding | Medium; plumbing | Low; plumbing |
| Availability of Material | yes | Yes | yes | Yes |
| Durability | Very high >20 years | High; drum is weakness | Medium; Depending on chosen liner | medium |
| Agitation | Self agitated by Biogas pressure | Manual steering | Not possible; plug flow type | Evtl Manual steering |
| Sizing | 6 to 124 m³ digester vol | Up to 20 m³ | Combination possible | Up to 6 m³ digester vol |
| Methane emission | High | Medium | Low | Medium |
GET MORE INFORMATION
ADVANTAGES OF USING BIOGAS

- Biogas is Eco-Friendly.
- Biogas Generation Reduces Soil and Water Pollution.
- Biogas Generation Produces Organic Fertilizer.
- It’s A Simple and Low-Cost Technology
- It encourages a circular economy.
- Healthy Cooking Alternative for Developing Areas.
SOURCES OF BIOMASS
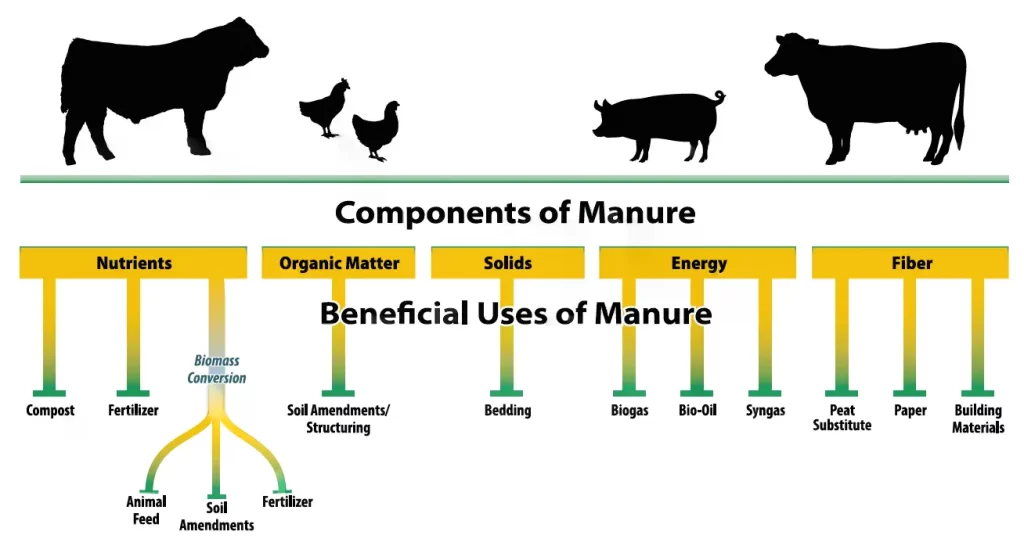
The raw materials used for the generation of biogas in our biodigesters include;
- Solid leftover food
- Vegetable waste
- Milk products
- Roots, tubers, peels
- Livestock waste such as cow dung, poultry droppings, etc
GET AN EXPERTS OPINION
Our team would like to talk to you and see where we can help












Good day
I am interested in your biogas solutions for resell.
I, interested in putting up biogas for home use, with 1 cow and 3 goats. is it possible .
VERY informative and enlightening, please include cost estimates with regard to distance from your area of manufacture to various counties ,like maybe Nairobi, Mombasa ,Kisumu Eldoret, Busia, Malindi e.t.c
IAM interested in your products more so biogas
Send me Prices for various type of product